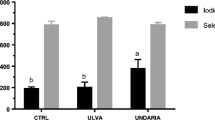
Abstract
Senegalese sole is one of the most promising fish species cultivated in the Southern European countries. This study was aimed at assessing the effects of microalgae biomass added to diets for Senegalese sole juveniles on fish growing and condition status. Three isoproteic (52%) and isolipidic (10%) were formulated containing 15% Tisochrysis lutea (TISO), Nannochloropsis gaditana (NAN), or Scenedesmus almeriensis (SCE) biomass, respectively. An experimental microalgae-free diet (CT) and a commercial diet (COM) were used as controls. Fish were fed at 3% of their body weight for 85 days. Final body weight of fish fed microalgae-supplemented diets did not differ from group fed CT diet. Fish-fed CT, TISO, NAN, and SCE showed higher growth performance and nutrient utilization figures than specimen-fed COM diet. The highest carcass lipid content was found in COM group (141 g kg−1), and no differences were observed in body protein content. Ash was significantly higher in TISO, NAN, and SCE groups compared to fish-fed CT. Muscle EPA and DHA contents were not modified owing to the different dietary treatments. The n3/n6 and EPA/DHA ratios in muscle were similar in all the experimental groups. The quantification of digestive proteolytic activities did not differ among experimental groups, although differences in the protease pattern in digestive extracts by zymography were revealed in those fish fed on COM diet. Both α-amylase activity in the intestinal lumen and leucine aminopeptidase in the intestinal tissue were significantly lower in COM fish. Specimens fed on SCE diet showed a higher leucine aminopeptidase activity associated to the intestinal tissue compared to NAN-fed fish (0.40 and 0.25 U g tissue−1, respectively). The ultrastructural study revealed that the dietary inclusion of algal biomass, especially T. lutea and N. gaditana, had a positive impact on the absorptive capacity of the intestinal mucosa. The highest values for the parameters microvilli length and microvilli absorption surface were observed in fish fed on NAN diet (1.99 μm and 45.93 μm2, respectively). Even though further studies aimed at optimizing commercial formulas for Senegalese sole are required prior to any large-scale practical utilization, the results obtained clearly suggest the potential of microalgae as dietary ingredients for this fish species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcón FJ, Díaz M, Moyano FJ, Abellán E (1998) Characterization and functional properties of digestive proteases in two sparids; gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and common dentex (Dentex dentex). Fish Physiol Biochem 19(3):257–267. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007717708491
Andersen NG, Alsted NS (1993) Growth and body composition of turbot (Scopthalmus maximus L.) in relation to different lipid/protein ratios in the diet. In: Kaushik SJ, Luquet P (eds) Fish nutrition in practice. INRA, Paris, pp 479–491
Association of Analytical Chemists (2000) Official methods of analysis of official analytical chemists international, 17th edn. Association of Analytical Chemists (AOAC), Washington, DC
Barroso FG, Rodiles A, Vizcaíno AJ, Martínez TF, Alarcón FJ (2013) Evaluation of feed attractans in juvenile Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis. J World Aquacult Soc 44(5):682–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.12068
Bell JG, Henderson RJ, Tocher DR, McGhee F, Dick JR, Porter A, Smullen RP, Sargent JR (2002) Substituting fish oil with crude palm oil in the diet of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) affects muscle fatty acid composition and hepatic fatty acid metabolism. J Nutr 132(2):222–230
Bergmeyer HV (1974) Phosphatases methods of enzymatic analysis, vol. 2. Academic Press, New York
Borges P, Oliveira B, Casal S, Dias J, Conceição L, Valente LMP (2009) Dietary lipid level affects growth performance and nutrient utilisation of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles. Br J Nutr 102(07):1007–1014. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114509345262
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgramquantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1-2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Burr GS, Barrows FT, Gaylord G, Wolters WR (2011) Apparent digestibility of macronutrients and phosphorus in plant derived ingredients for Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar and Arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus. Aquac Nutr 17(5):570–577. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2011.00855.x
Cabral EM, Bacelar M, Batista S, Castro-Cunha M, Ozório ROA, Valente LMP (2011) Replacement of fishmeal by increasing levels of plant protein blends in diets for Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles. Aquaculture 322–323:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.09.023
Cabral EM, Fernandes TJR, Campo SD, Castro-Cunha M, Oliveira MBPP, Cunha ML, Valente LMP (2013) Replacement of fish meal by plant protein ingredientssources up to 75% induces good growth performance without affecting flesh quality in on growing Senegalese sole. Aquaculture 380–383:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.12.006
Chen MY, Ye JD, Yang W, Wang K (2013) Growth, feed utilization and blood metabolic responses to different amylase-amylopectin ratio fed diets in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Asian Australas J Anim Sci 26(8):1160–1171. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2013.13022
Christie WW (1982) A simple procedure for rapid transmethylation of glycerolipids and cholesteryl esters. J Lipid Res 23(7):1072–1075
DelMar EG, Largman C, Broderick JW, Geokas MC (1979) A sensitive new substrate for chymotrypsin. Anal Biochem 99(2):316–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(79)80013-5
Dias J, Rueda-Jasso R, Panserat S, da Conceiçao LEC, Gomes EF, Dinis MT (2004) Effect of dietary carbohydrate to lipid ratios on growth, lipid deposition and metabolic hepatic enzymes in juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup). Aquac Res 35(12):1122–1130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2004.01135.x
Dinis MT, Ribeiro L, Soares F, Sarasquete C (1999) A review of the cultivation potential of Solea senegalensis in Spain and in Portugal. Aquaculture 176(1-2):27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00047-2
Erlanger B, Kokowsky N, Cohen W (1961) The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys 95(2):271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-X
Fernandes TJR, Alves RC, Souza T, Silva JMG, Castro-Cunha M, Valente LMP, Oliveira MBPP (2012) Lipid content and fatty acid profile of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) juveniles as affected by feed containing different amounts of plant protein sources. Food Chem 134(3):1337–1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.026
Fournier V, Huelvan C, Desbruyeres E (2004) Incorporation of a mixture of plant feedstuffs as substitute for fish meal in diets of juvenile turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture 236(1-4):451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.01.035
Frías-Quintana CA, Álvarez-González CA, Tovar-Ramírez D, Martínez-García R, Camarillo-Coop S, Peña E, Galaviz MA (2017) Use of potato starch in diets of tropical gar (Atractosteus tropicus, Gill 1863) larvae. Aust Fish 2(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes2010003
Gatta PP, Parma L, Guarniero I, Mandrioli L, Sirri R, Fontanillas R, Bonaldo A (2011) Growth, feed utilization and liver histology of juvenile common sole (Solea solea L.) fed isoenergetic diets with increasind protein levels. Aquac Res 42(3):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02622.x
Güroy BK, Cirik S, Güroy D, Sanver F, Tekinay AA (2007) Effects of Ulva rigida or Cystoseira barbata meals as a feed additive on growth performance, feed utilization, and body composition in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 31:91–97
Hu CH, Xu Y, Xia MS, Xiong L, Xu ZR (2007) Effects of Cu2+ - exchanged montmorillonite on growth performance, microbial ecology and intestinal morphology of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 270:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.01.027
Hussein EE-S, Dabrowski K, El-Saidy DMSD, Lee B-J (2013) Enhancing the growth of Nile tilapia larvae/juveniles by replacing plant (gluten) protein with algae protein. Aquac Res 44(6):937–949. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2012.03100.x
Imsland AK, Foss A, Conceiçao LEC, Dinis MT, Delbare D, Schram E, Kamstra A, Rema P, White P (2003) A review of the culture potential of Solea solea and S. senegalensis. Rev Fish Biol Fish 13(4):379–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-004-1632-6
Kiron V, Sorensen M, Huntley M, Vasanth GK, Gong Y, Dahle D, Palihawadana AM (2016) Deffated biomas of the microalga, Desmodesmus sp., can replace fishmeal in the feeds for Atlantic salmon. Front Mar Sci 3:67. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2016.00067
Kumar V, Sahu NP, Kumar S, Gupta SK (2008) Gelatinized to non-gelatinized starch ratio in the diet of Labeo rohita: effect on digestive and metabolic response and on growth. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 92(4):492–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2007.00739.x
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Lepage G, Roy CC (1984) Improved recovery of fatty acid through direct transesterification without prior extraction or purification. J Lipid Res 25(12):1391–1396
Lin S, Luo L (2011) Effects of different levels of soybean meal inclusion in replacement for fishmeal on growth, digestive enzymes and transaminase activities in practical diets for juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus. Anim Feed Sci Technol 168(1-2):80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2011.03.012
Liu XH, Ye CX, Ye JD, Shen BD, Wang CY, Wang AL (2014) Effects of dietary amylose/amylopectin ratio on growth performance, feed utilization, digestive enzymes, and postprandial metabolic responses in juvenile obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus. Fish Physiol Biochem 40(5):1423–1436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9937-4
Lupatsch I (2009) Quantifying nutritional requirements in aquaculture—the factorial approach. In: Burnell G, Allan G (eds) New Technologies in Aquaculture: improving production efficiency, quality and environmental management. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 417–439
Martins D, Valente LMP, Lall SP (2007) Effects of dietary lipid level on growth and lipid utilization by juvenile Atlantic halibut (H. hippoglossus L.) Aquaculture 263(1-4):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.10.017
Merrifield DL, Dimitroglou A, Bradley G, Baker RTM, Davies SJ (2009) Soybean meal alters autochthonous microbial populations, microvilli morphology and compromises intestinal enterocyte integrity of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 32(9):755–766. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01052.x
Morais S, Cahu C, Zambonino-Infante JL, Robin J, Ronnestad I, Dinis MT, Conceicao LEC (2004) Dietary TAG source and level affect performance and lipase expression in larval sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Lipids 39(5):449–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-004-1250-2
Moreira N, Soares S, Valente LMP, Castro-Cunha M, Cunha LM, Guedes de Pinho P (2014) Effect of two experimental diets (protein and lipid vegetable oil blends) on the volatile profile of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) muscle. Food Chem 153:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.071
Murray HM, Lall SP, Rajaselvam R, Lee AB, Blanchard B, Flight RM, Colombo S, Mohindra V, Douglas SE (2010) A nutrigenomic analysis of intestinal response to partial soybean meal replacement in diets for juvenile Atlantic halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus, L. Aquaculture 298(3-4):282–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.11.001
Olsen RL, Hasan RM (2012) A limited supply of fish meal: impact on future increases in global aquaculture production. Trends Food Sci Technol 27(2):120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2012.06.003
Olsen RE, Myklebust R, Ringø E, Mayhew TM (2000) The influences of dietary linseed oil and saturated fatty acids on caecal enterocytes in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus L.): a quantitative ultrastructural study. Fish Physiol Biochem 22(3):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007879127182
Pereira TG, Oliva-Teles A (2003) Evaluation of corn gluten meal as a protein source in diets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) juveniles. Aquac Res 34:1111–1117
Pfleiderer G (1970) Particle-bound aminopeptidase from pig kidney. Methods Enzymol 19:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(70)19038-0
Pham MA, Lee KJ, Lim SJ, Park KH (2007) Evaluation of cottonseed and soybean meal as partial replacement for fishmeal in diets for juvenile Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Sci 73(4):760–769. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01394.x
Regost C, Arzel J, Cardinal M, Robin J, Laroche M, Kaushik SJ (2001) Dietary lipid level, hepatic lipogenesis and flesh quality in turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture 193(3-4):291–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00493-2
Reitan KI, Eriksen T, Berge GM, Ruyter B, Sørensen M, Galloway TF, Kjørsvik E (2013) Nutrient digestibility and effect on gut morphology of diets with increasing content of dried microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum in Atlantic cod and Atlantic salmon. Lecture presented at the 3rd Danish Macro Algae Conference, Grenaa, Denmark, 9th–10th October 2013 (http://www.algecenterdanmark.dk/conferences/)
Rema P, Conceiçao LEC, Evers F, Castro-Cunha M, Dinis MT, Dias J (2008) Optimal dietary protein levels in juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Aquac Nutr 14(3):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2007.00527.x
Rodiles A, Herrera M, Hachero-Cruzado I, Ruíz-Járabo I, Mancera JM, Cordero ML, Lall SP, Alarcón FJ (2015) Tissue composition, blood biochemistry and histology of digestive organs in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles fed diets containing different plant protein ingredients. Aquac Nutr 21(6):767–779. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12207
Rodríguez-Ruiz J, Belarbi EH, García JL, López D (1998) Rapid simultaneous lipid extraction and transesterification for fatty acid analyses. Biotechnol Tech 12(9):689–691. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008812904017
Rubio VC, Navarro DB, Madrid JA, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2009) Macronutrient self-selection in Solea senegalensis fed macronutrient diets and challenged with protein dilutions. Aquaculture 291(1-2):95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.02.040
Sáenz de Rodrigáñez MA, Díaz-Rosales P, Chabrillón M, Smidt H, Arijo S, León- Rubio JM, Alarcón FJ, Balebona MC, Moriñigo MA, Cara JB, Moyano FJ (2009) Effect of dietary administration of probiotics on growth and intestine functionally of juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup 1858). Aquac Nutr 15(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2008.00581.x
Santigosa E, Sánchez J, Médale F, Kaushik S, Pérez-Sánchez J, Gallardo MA (2008) Modifications of digestive enzymes in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and sea bream (Sparus aurata) in response to dietary fishmeal replacement by plant protein sources. Aquaculture 282(1-4):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.06.007
Silva FCP, Nicoli JR, Zambonino-Infante JL, Le Gall M, Kaushik S, Gatesoupe FJ (2010) Influence of partial substitution of dietary fishmeal on the activity of digestive enzymes in the intestinal brush border membrane of gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata and goldfish, Carassius auratus. Aquaculture 306(1-4):233–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.05.018
Sorensen M, Berge GM, Reitan KI, Ruyter R (2016) Microalgae Phaeodactylum tircornutun in feed for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)-effect on nutrient digestibility, growth and utilization of feed. Aquaculture 460:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.04.010
Spolaore P, Joannis-Cassan C, Duran E, Isambert A (2006) Commercial applications of microalgae. Review. J Biosci Bioeng 101(2):87–96. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.101.87
Teimouri M, Amirkolaie AK, Yeganeh S (2013) The effects of Spirulina platensis meal as a feed supplement on growth performance and pigmentation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 396-399:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.02.009
Tibaldi E, Chini Zittelli G, Parisi G, Bruno M, Giorgi G, Tulli F, Venturini S, Tredici MR, Poli BM (2015) Growth performance and quality traits of European sea bass (D. labrax) fed diets including increasing levels of freeze-dried Isochrysis sp. (T-ISO) biomass as a source of protein and n-3 long chain PUFA in partial substitution of fish derivatives. Aquaculture 440:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.02.002
Tocher DR (2003) Metabolism and functions of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish. Rev Fish Sci 11(2):107–184. https://doi.org/10.1080/713610925
Torzillo G, Pushparaj B, Bocci F, Balloni W, Materassi R, Florenzano G (1986) Production of Spirulina biomass in closed photobioreactors. Biomass 11(1):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-4565(86)90021-1
Valente LMP, Linares F, Villanueva JLR, Silva JMG, Espe M, Escórcio C, Pires MA, Saavedra MJ, Borges P, Medale F, Alvarez-Blázquez B, Peleteiro JB (2011) Dietary protein source or energy levels have no major impact on growth performance, nutrient utilisation or flesh fatty acids composition of market-sized Senegalese sole. Aquaculture 318(1-2):128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.05.026
Vizcaíno AJ, López G, Sáez MI, Jiménez JA, Barros A, Hidalgo L, Camacho-Rodríguez J, Martínez TF, Cerón-García MC, Alarcón FJ (2014) Effects of the microalga Scenedesmus almeriensis as fishmeal alternative in diets for gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata, juveniles. Aquaculture 431:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.05.010
Vizcaíno AJ, Saéz MI, López G, Arizcun M, Abellán E, Martínez TF, Cerón-García MC, Alarcón FJ (2016) Tetraselmis suecia and Tisochrysis lutea meal as dietary ingredients for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) fry. J Appl Phycol 28(5):2843–2855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0845-0
Walker AB, Berlinsky DL (2011) Effects of partial replacement of fishmeal protein by microalgae on growth, feed intake, and body composition of Atlantic cod. N Am J Aquac 73:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/15222055.2010.549030
Acknowledgements
The experimental diets were made in the facilities provided by CEIA3 and CEIMAR (Service of Experimental Diets; http://www.ual.es/stecnicos_spe). The authors acknowledge Fundación Cajamar (Almería, Spain) for kindly providing the microalgae used in this work.
Funding
This study was part of the research projects ECOAQUA, AGR5334, and SABANA (grant # 727874) from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vizcaíno, A.J., Rodiles, A., López, G. et al. Growth performance, body composition, and digestive functionality of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) juveniles fed diets including microalgae freeze-dried biomass. Fish Physiol Biochem 44, 661–677 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0462-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0462-8